Overview
AlgoBase is a desktop algorithmic problem manager. The user interacts with it using a CLI, and it has a GUI created with JavaFX. It is written in Java, and has about 20 kLoC.
Summary of contributions
-
Code contributed: [View on RepoSense]
-
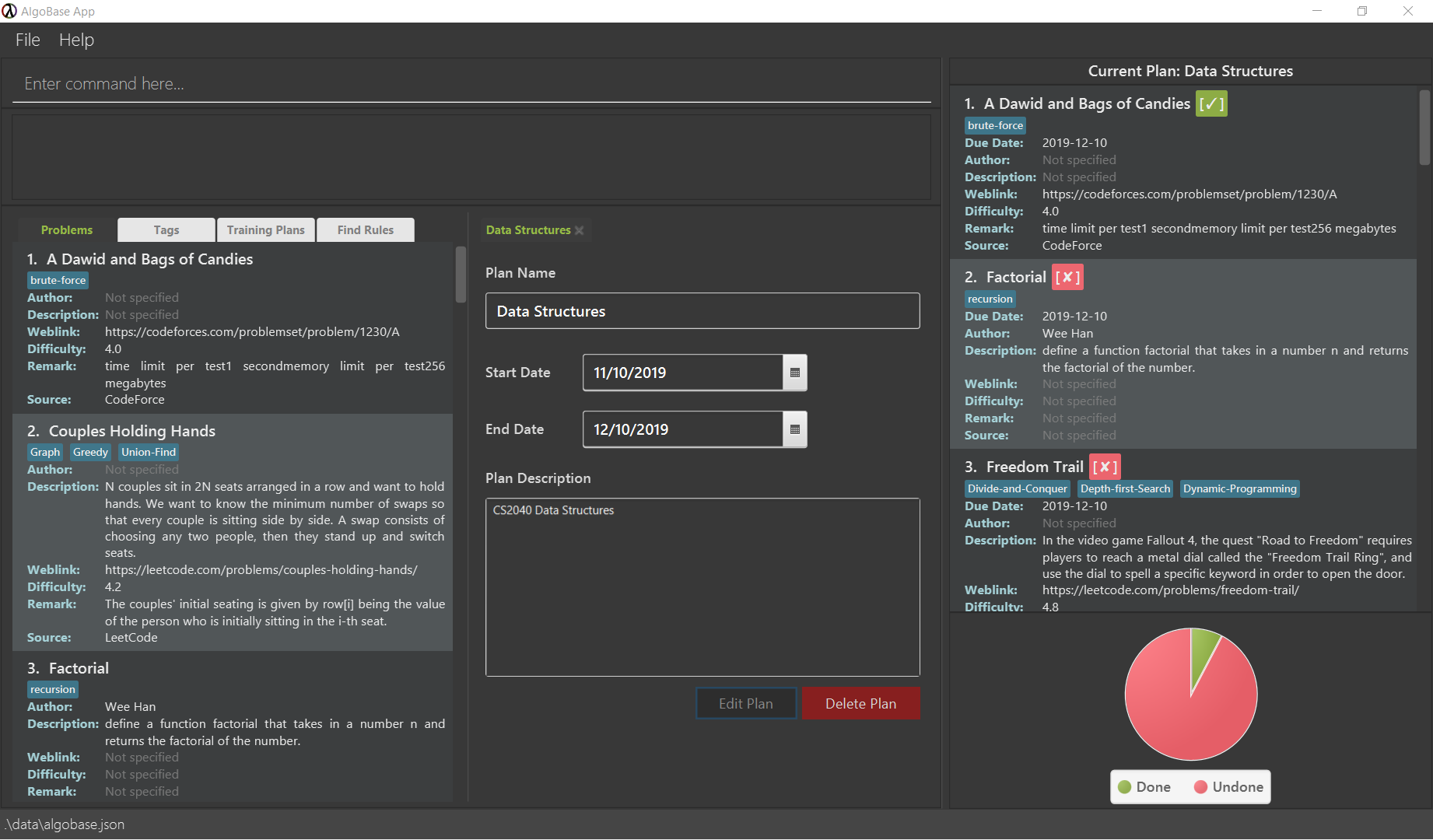
Major enhancement: Implemented task management feature
-
What it does: This feature allows the user to keep track of the problems to be done as upcoming tasks in separate plans and thus manage his/her progress for each plan.
-
Justification: Task management is the core feature of AlgoBase. It allows the user to manage the problems as tasks in separate plans for different purposes, such as interviews for different companies or different rounds, instead of managing all problems stored in the database all together. By introducing the notion of tasks, user can add more details to the problems such as due dates and whether each problem has been done, without modifying the original problems. This adds significant value to AlgoBase as an algorithmic problem manager.
-
Highlights:
-
This feature involves full-stack development in all five main components in AlgoBase, including
Logic,Model,Storage,UiandUiLogic. -
This feature is highly coupled with the problem tracking feature and training plan feature. It requires in-depth analysis of all existing features in order to avoid unintended behaviours.
-
For example, since each task stores a problem, when a problem is deleted or updated, all corresponding tasks in all plans need to be deleted or updated simultaneously.
-
Moreover, to avoid user mistakes when deleting problems that are used in some tasks, which may cause additional overhead to bring back the tasks, a distinction between normal mode and "forced" mode is introduced to reduce such risks. (User command to delete problems that are used in tasks will fail gracefully, unless a "forced" flag is added to the end of the command to enable "forced" mode.)
-
A task management pane is also added in the main display to allow user direct and convenient access to the current plan he/she is doing.
-
-
Relevant pull requests: #62 #70 #73 #75 #116 #143 #150 #164 #210 #237
-
-
Minor enhancement: Implemented data management feature
It allows the user to export their data into JSON format and import new data from JSON files. -
Other contributions:
-
Project management:
-
Managed releases
v1.1,v1.3.2andv1.3.3(3 releases) on GitHub -
Updated logo of AlgoBase
-
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Implement relational storage of models in database [#80]
This allows integrity check on the storage file upon each launch of AlgoBase.
-
-
Documentation:
-
Updated documentation for UI, Logic and Storage in Developer Guide
-
Added documentation for Task Management feature in Developer Guide and User Guide
-
-
Community:
-
Tools:
-
Integrated Github plugins (AppVeyor, Coveralls, Netlify, Travis) to the team repository
-
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
Task Management
Adding new tasks: addtask
Adds a task to a specified plan.
Format: addtask plan/PLAN_INDEX prob/PROBLEM_INDEX [due/DUE_DATE]
-
The target plan should not contain tasks with the same problem as the one identified by
PROBLEM_INDEX. -
DUE_DATEshould be in the format ofyyyy-MM-dd -
DUE_DATEshould be in between plan’s start date and end date (inclusive).
DUE_DATE will be set to the end date of the plan to be added into, if unspecified.
|
Examples:
-
addtask plan/1 prob/1 due/2019-12-12
Creates a new task with the first problem in the displayed problem list and due date on 12 December 2019, and adds it the first plan in the displayed plan list.
Copying tasks between plans: copytask
Copies a specified task from one plan to another.
Format: copytask task/TASK_INDEX from/PLAN_FROM_INDEX to/PLAN_TO_INDEX
-
Task identified by
TASK_INDEXshould have a due date in between the start date and end date of the plan identified byPLAN_TO_INDEX(inclusive). -
Plan identified by
PLAN_TO_INDEXshould not contain tasks that consist of the same problem as the task identified byTASK_INDEX.
Examples:
-
copytask task/1 from/1 to/2
Copies the first task in the first plan to the second plan in the displayed plan list.
Deleting tasks: deletetask
Deletes a specified task from a specified plan.
Format: deletetask plan/PLAN_INDEX task/TASK_INDEX
Examples:
-
deletetask plan/1 task/1
Deletes the first task in the first plan to the second plan in the displayed plan list.
Marking tasks as done: donetask
Marks a specified task in a specified plan as done.
Format: donetask plan/PLAN_INDEX task/TASK_INDEX
-
The task to be marked as done should have a current status of
undone.
Examples:
-
donetask plan/1 task/1
Marks the first task in the first plan as done.
Editing due date of tasks: edittask
Edits the due date of a specified task from a specified plan.
Format: edittask plan/PLAN_INDEX task/TASK_INDEX due/DUE_DATE
-
DUE_DATEshould be in the format ofyyyy-MM-dd -
DUE_DATEshould be in between plan’s start date and end date (inclusive).
Examples:
-
edittask plan/1 task/1 due/2019-12-12
Changes the due date of the first task in the first plan to 12 December 2019.
Moving tasks between plans: movetask
Moves a specified task from a specified plan to another.
Format: movetask task/TASK_INDEX from/PLAN_FROM_INDEX to/PLAN_TO_INDEX
-
Task identified by
TASK_INDEXshould have a due date in between the start date and end date of the plan identified byPLAN_TO_INDEX(inclusive). -
Plan identified by
PLAN_TO_INDEXshould not contain tasks that consist of the same problem as the task identified byTASK_INDEX.
Examples:
-
movetask task/1 from/1 to/2
Removes the first task from the first plan and adds it to the second plan in the displayed plan list.
Setting current plan: setplan
Sets a specified plan as the current plan in main display.
Format: setplan PLAN_INDEX
Examples:
-
setplan 10
Sets plan with index 10 as the current plan.
Marking tasks as undone: undonetask
Marks a specified task in a specified plan as undone.
Format: undonetask plan/PLAN_INDEX task/TASK_INDEX
-
The task to be marked as undone should have a current status of
done.
Examples:
-
undonetask plan/1 task/1
Marks the first task in the first plan as undone.
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
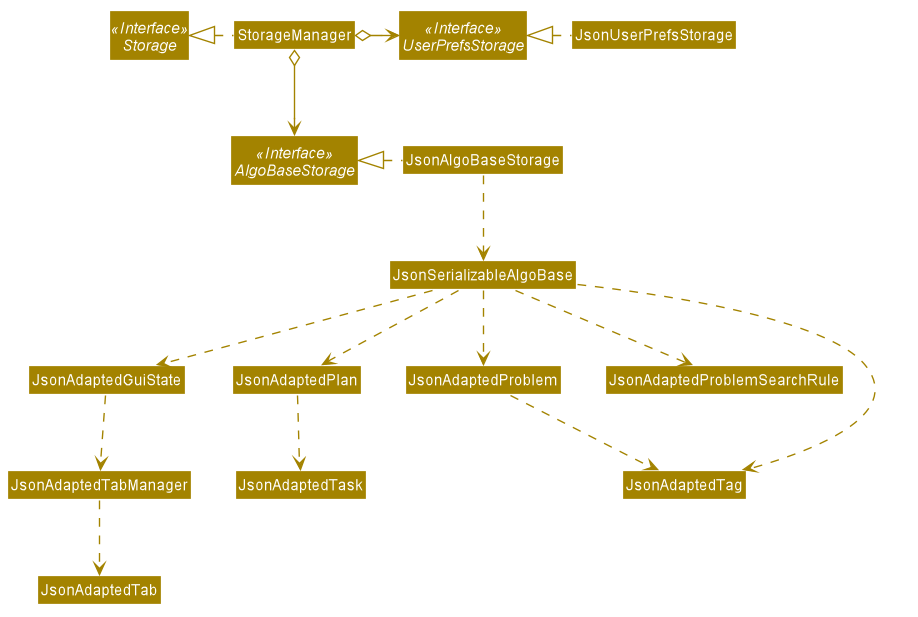
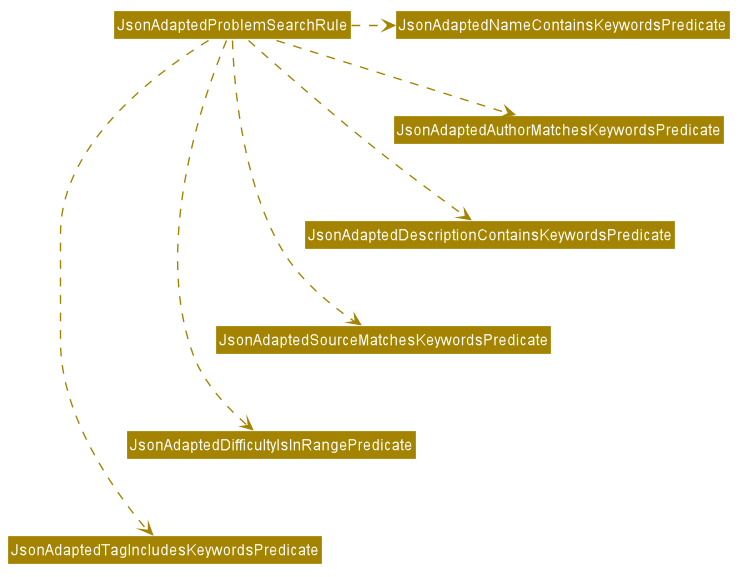
Storage component
API :
Storage.java
The Storage component,
-
can store
UserPrefsobjects inJSONformat. -
can retrieve
UserPrefsobjects fromJSONformat. -
can store the AlgoBase app data including
GuiState,Plan,Problem,ProblemSearchRule,Tag,Taskobjects in relational manner inJSONformat. -
can retrieve
GuiState,Plan,Problem,ProblemSearchRule,Tag,Taskobjects from data stored inJSONformat.
UI component
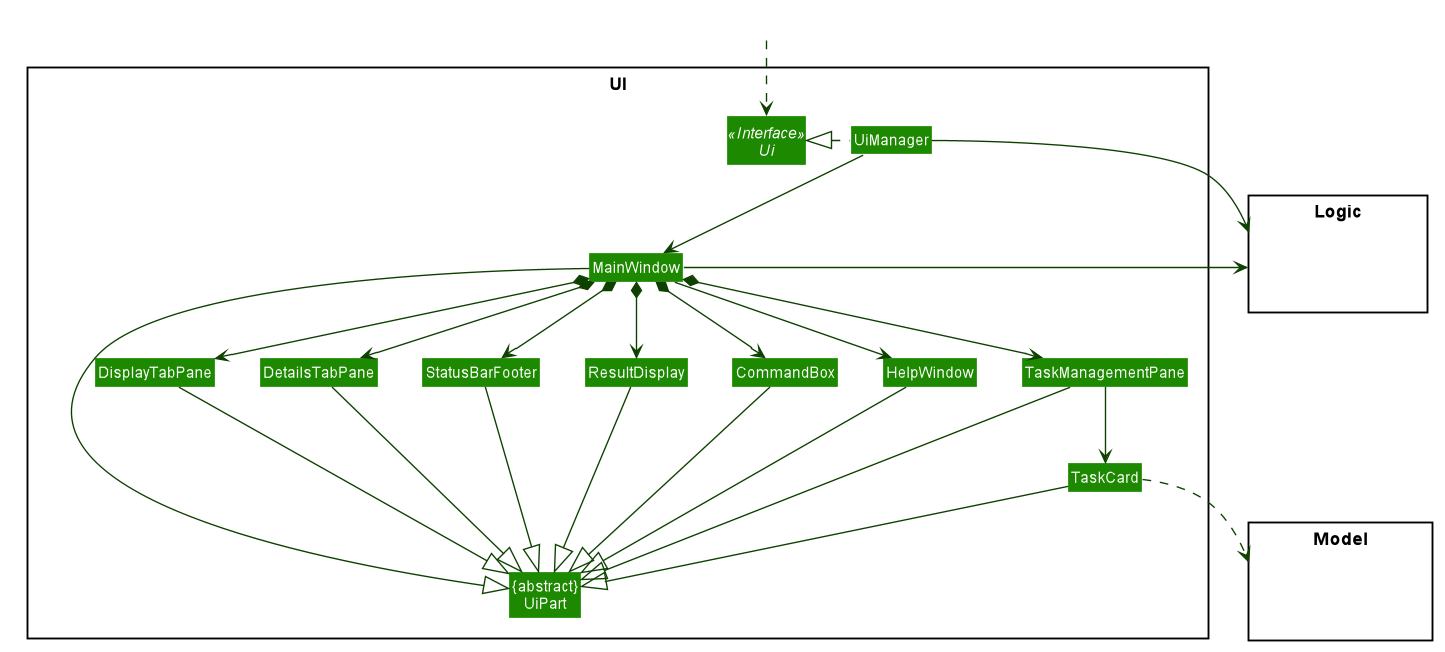
API :
Ui.java
The UI component consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts
e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, DetailsTabPane, DisplayTabPane, TaskManagementPane, StatusBarFooter etc.
All these components, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The DetailsTabPane consists of FindRuleListPanel, PlanListPanel, ProblemListPanel and TagListPanel,
which are used for displaying entries of FindRule, Plan, Problem and Tag stored in AlgoBase respectively.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework.
The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder.
For example, the layout of the MainWindow
is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
-
Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. -
Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
Task Management Feature
As an algorithmic problem management tool, one of the most important features will be managing tasks that have been done or are to be done.
This section will describe in details the current implementation and design considerations of the task management feature.
Current Implementation
The task management feature supports eight main operations:
-
AddTask- creates a new task for a problem and add it to a specified plan. -
CopyTask- copies a task from one plan to another. -
DeleteTask- deletes an existing task from a specified plan. -
DoneTask- marks a task as done in a specified plan. -
EditTask- edits the due date of a task in a specified plan. -
MoveTask- moves a task from one plan to another. -
SetPlan- sets a plan as the current plan in main display. -
UndoneTask- marks a task as undone in a specified plan.
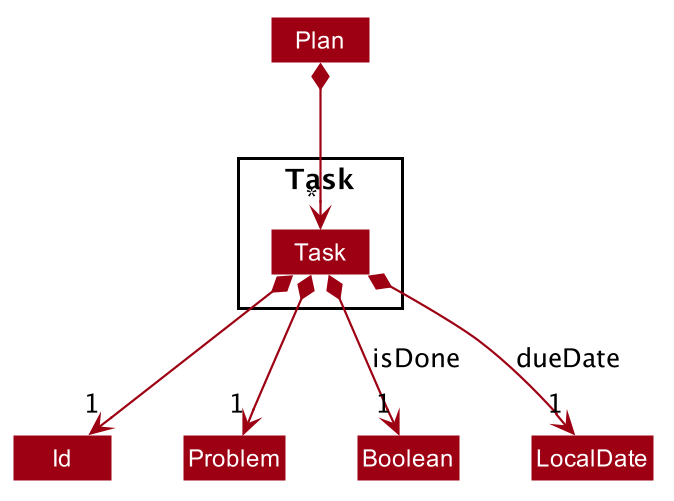
This feature is mainly supported by the Task class.
Given below is the class diagram of the Task class.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the mechanism for adding tasks behaves at each step.
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes the AddTaskCommand:
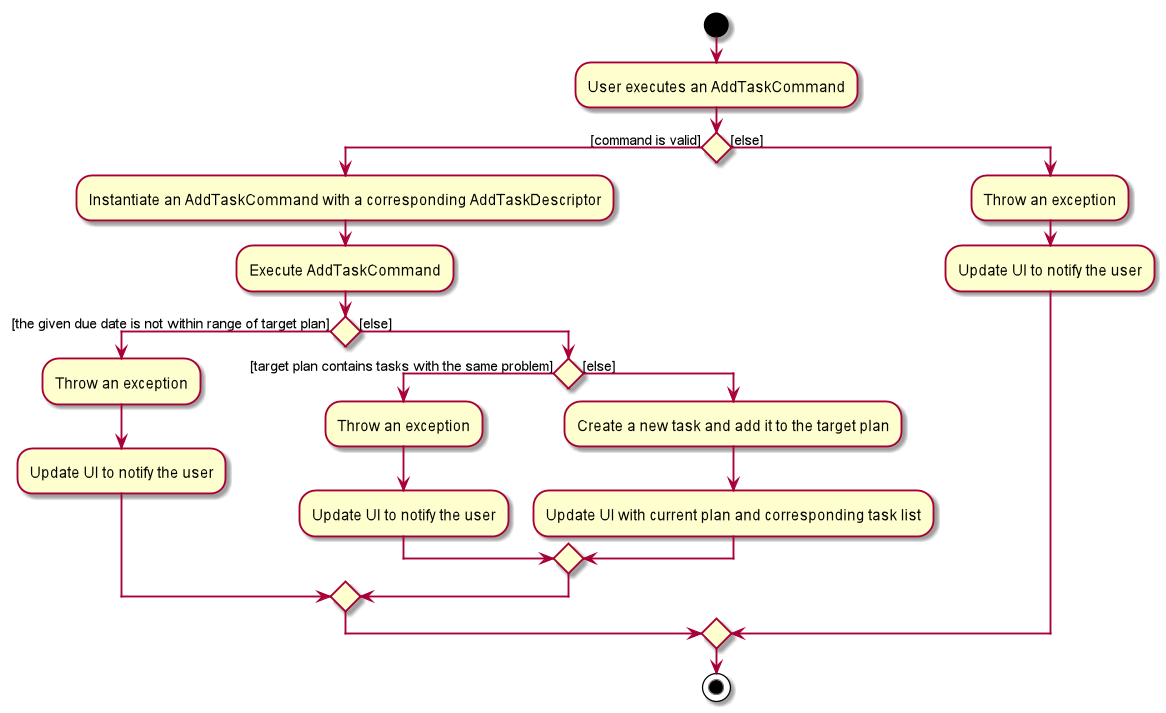
AddTaskCommandStep 1. The user launches the application.
Step 2. AlgoBase displays a list of existing problems and plans in the UI.
Step 3. The user executes addtask plan/1 prob/1 to add the problem with index 1 in the list to the plan with index 1.
The AddTaskCommand calls Model#updateTasks to create a new plan from the original plan with this additional task,
and replace the original plan with this updated plan in the PlanList stored in AlgoBase.
The sequence diagram below shows the high-level abstraction of how AlgoBase processes user request
to execute addtask plan/1 prob/1:
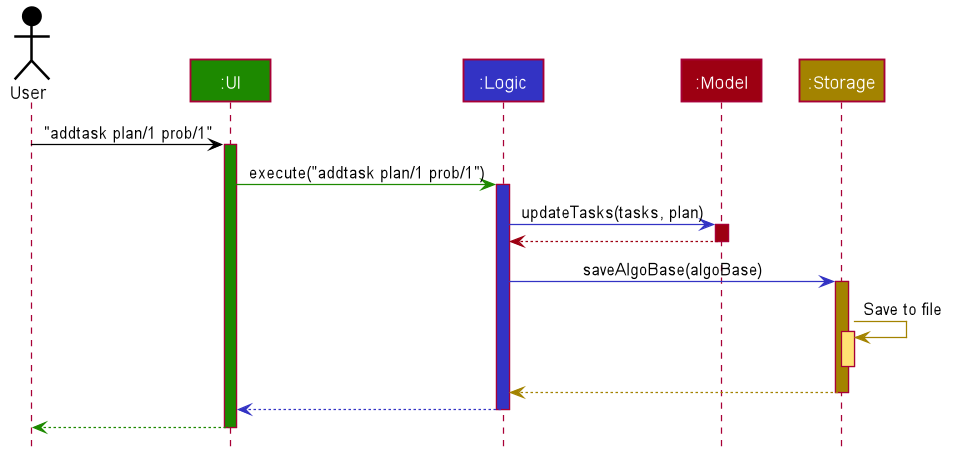
addtask plan/1 prob/1The following sequence diagram illustrates the interaction between the Logic and Model components
while executing AddTaskCommand:
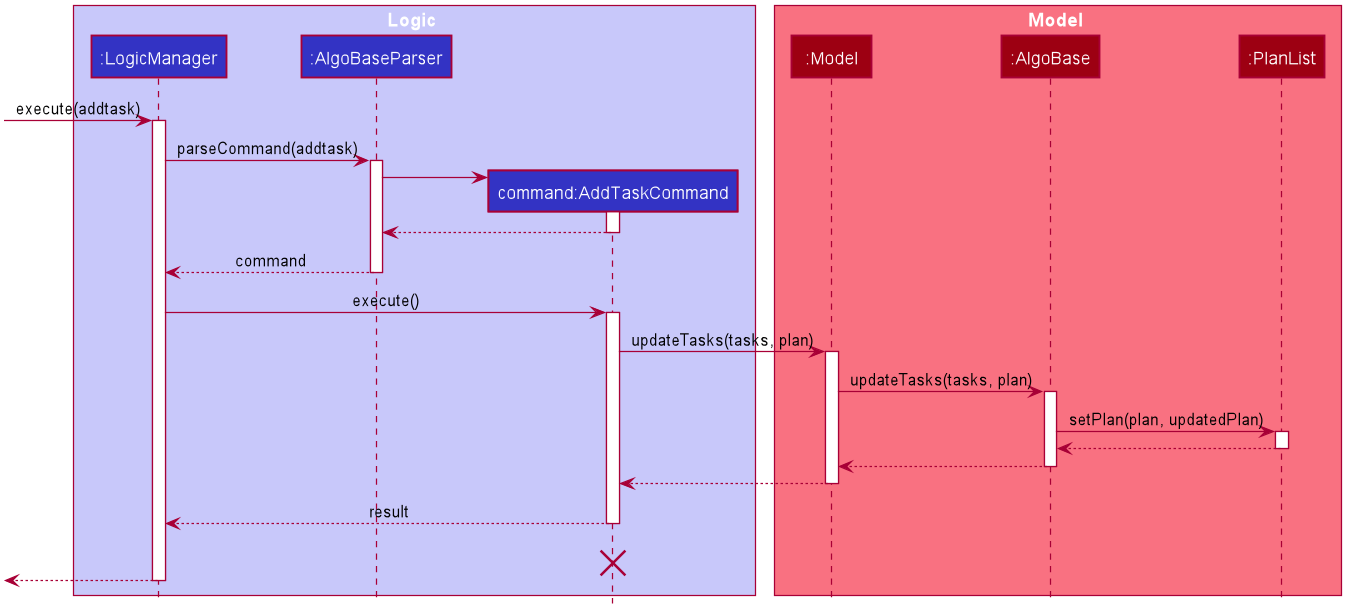
AddTaskCommandDesign Considerations
Aspect: Data structure to support the task commands.
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use a
HashSetto store tasks in a plan.-
Pros: Duplicate tasks can be checked easily.
-
Cons: Harder to identify tasks by index.
-
-
Alternative 2: Use an
ArrayListto store tasks in a plan.-
Pros: Tasks can be identified by index easily.
-
Cons: Harder to check for duplicate tasks.
-
Aspect: How to store problem details within tasks to support the task commands.
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Store a problem object in each task.
-
Pros: Changes in problem details will be reflected in the relevant tasks as well.
-
Cons: Relational storage is required to keep track of this relationship.
-
-
Alternative 2: Copy all problem details and store as separate fields in each task.
-
Pros: No need to implement relational storage. There will be less coupling between problems and tasks as well.
-
Cons: Changes in problem details cannot be reflected in the relevant tasks easily.
-
Aspect: Relational storage to support the task commands.
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use an additional
idfield to identify problems and tasks.-
Pros: The id field is kept immutable over time, thus ensuring integrity.
-
Cons: An additional field is needed for the models.
-
-
Alternative 2: Use object hash to identify problems and tasks.
-
Pros: No need to store another additional field in the models.
-
Cons: Object hash can change over time.
-
PROJECT: SourceCast
SourceCast is an interactive code recorder and player to support e-teaching and e-learning, used in Source Academy, an immersive experiential learning environment for NUS freshman programming methodology course, CS1101S.